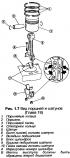
4-cylinder car engine Audi 80 B3, petrol
Engine Specifications
Total information Code designations: 1.6 l - RN 1.8 l - RU, DZ, NE, PM, JN 2.0 l - FOR Working volume: 1.6 l - 1595 cm 3 1.8 l - 1781cm 3 2.0 l - 1984 cm 3...
Total information Code designations: 1.6 l - RN 1.8 l - RU, DZ, NE, PM, JN 2.0 l - FOR Working volume: 1.6 l - 1595 cm 3 1.8 l - 1781cm 3 2.0 l - 1984 cm 3...
General description of the engine
The engine is a 4-cylinder, in-line with an overhead camshaft, traditionally installed in front of the car. The crankshaft has five main bearings, the center...
The engine is a 4-cylinder, in-line with an overhead camshaft, traditionally installed in front of the car. The crankshaft has five main bearings, the center...
Engine Maintenance
Perform the following procedures at the intervals given in the 'Maintenance' Section at the beginning of the Manual. Change engine oil and oil filter 1. To...
Perform the following procedures at the intervals given in the 'Maintenance' Section at the beginning of the Manual. Change engine oil and oil filter 1. To...
Basic actions possible with the engine
In the car (a) Removing the camshaft and timing belt (b) Removal and maintenance of the cylinder head (c) Removing flywheel/drive plate (after removing the...
In the car (a) Removing the camshaft and timing belt (b) Removal and maintenance of the cylinder head (c) Removing flywheel/drive plate (after removing the...
Engine — removal and installation
1. Remove the hood as described in Section 11 . 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable. 3. Unscrew and remove the mudguard from under the engine. 4. Place a...
1. Remove the hood as described in Section 11 . 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable. 3. Unscrew and remove the mudguard from under the engine. 4. Place a...
Engine disassembly — general description
1. If possible, place the engine on a table. Two to three wooden beams will be required to support the engine in a standing position 2. Cleanliness is very...
1. If possible, place the engine on a table. Two to three wooden beams will be required to support the engine in a standing position 2. Cleanliness is very...
Auxiliary parts — removal and installation
By removing the engine from the vehicle, the external accessories listed in the following list can be removed. The order of removal does not matter. intake and...
By removing the engine from the vehicle, the external accessories listed in the following list can be removed. The order of removal does not matter. intake and...
Engine — complete disassembly
1. Mark the position of the flywheel relative to the end of the crankshaft. 2. Loosen the flywheel/drive plate bolts. Temporarily insert a bolt into the...
1. Mark the position of the flywheel relative to the end of the crankshaft. 2. Loosen the flywheel/drive plate bolts. Temporarily insert a bolt into the...
Toothed belt drive and asterisks — removal, inspection and installation
1. Remove the radiator ( Section 2 ), and drive belts for the alternator, power steering pump and air conditioning compressor (if available). 2. Disconnect the...
1. Remove the radiator ( Section 2 ), and drive belts for the alternator, power steering pump and air conditioning compressor (if available). 2. Disconnect the...
Camshaft and pushers — removal, inspection and installation
1. If the hydraulic tappets are noisy when the engine is warmed up to normal operating temperature, the following method will identify the faulty tappet....
1. If the hydraulic tappets are noisy when the engine is warmed up to normal operating temperature, the following method will identify the faulty tappet....
Cylinder head — removal and installation
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. 2. Drain the cooling system as described in Section 2 . 3. Remove intake and exhaust manifolds ( see Section 3 ),...
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. 2. Drain the cooling system as described in Section 2 . 3. Remove intake and exhaust manifolds ( see Section 3 ),...
Cylinder head — bulkhead
1. Having removed the cylinder head as previously described, the valves can be removed as follows. The valves are deeply inserted into the top of the cylinder...
1. Having removed the cylinder head as previously described, the valves can be removed as follows. The valves are deeply inserted into the top of the cylinder...
Flywheel / drive disc — removal, inspection and installation
1. On manual transmission models, remove the gearbox ( Section 6 ) and grip ( Section 5 ). 2. On models with automatic transmission, remove the automatic...
1. On manual transmission models, remove the gearbox ( Section 6 ) and grip ( Section 5 ). 2. On models with automatic transmission, remove the automatic...
Intermediate shaft — removal, inspection and installation
1. Remove the distributor (Section 4), and on carburetor models the fuel pump (Section 3). 2. Remove the toothed drive belt as described in Chapter 10 , but do...
1. Remove the distributor (Section 4), and on carburetor models the fuel pump (Section 3). 2. Remove the toothed drive belt as described in Chapter 10 , but do...
Pallet — removal and installation
1. Apply the parking brake, then jack up the front of the vehicle and support it on axle stands placed under the bottom. 2. Unscrew and remove the mudguard...
1. Apply the parking brake, then jack up the front of the vehicle and support it on axle stands placed under the bottom. 2. Unscrew and remove the mudguard...
Front and rear crankshaft oil seals — replacement
Front oil seal 1. Remove the timing belt and crankshaft sprocket as described in Chapter 10 . 2. If a special tool is available, the oil seal can be replaced...
Front oil seal 1. Remove the timing belt and crankshaft sprocket as described in Chapter 10 . 2. If a special tool is available, the oil seal can be replaced...
Oil pump — removal, inspection and installation
1. Remove the drip tray as described in Chapter 16 . 2. Using a socket wrench, unscrew the bolts and remove the suction tube from the oil pump. Remove the...
1. Remove the drip tray as described in Chapter 16 . 2. Using a socket wrench, unscrew the bolts and remove the suction tube from the oil pump. Remove the...
Pistons and connecting rods — removal and disassembly
1. Remove the cylinder head ( Chapter 12 ), pallet ( Chapter 16 ) and oil pump ( Chapter 18 ). 2. Rotate the engine so that the No. 1 connecting rod journal is...
1. Remove the cylinder head ( Chapter 12 ), pallet ( Chapter 16 ) and oil pump ( Chapter 18 ). 2. Rotate the engine so that the No. 1 connecting rod journal is...
Pistons and cylinder channels — check
1. Examine the condition of the pistons and cylinder bores. If they are in satisfactory condition, perform the following checks. 2. Measure the piston diameter...
1. Examine the condition of the pistons and cylinder bores. If they are in satisfactory condition, perform the following checks. 2. Measure the piston diameter...
Pistons and connecting rods — assembly and installation
1. Heat the piston in hot water, then insert the connecting rod and push the pin (photo). Make sure the tab marks on the connecting rod and the arrow on the...
1. Heat the piston in hot water, then insert the connecting rod and push the pin (photo). Make sure the tab marks on the connecting rod and the arrow on the...
Crankshaft and main bearings — check
1. Clean and check the condition of the crankshaft. 2. Check the wear of the connecting rod and main journals. If the engine has high mileage, or if there is...
1. Clean and check the condition of the crankshaft. 2. Check the wear of the connecting rod and main journals. If the engine has high mileage, or if there is...
Engine mounting brackets — replacement
1. Unscrew the front support beam from the block. 2. Support the weight of the engine with a winch. 3. Loosen the mounting nuts, then lift the motor and remove...
1. Unscrew the front support beam from the block. 2. Support the weight of the engine with a winch. 3. Loosen the mounting nuts, then lift the motor and remove...
Engine assembly — general description
To ensure maximum performance and minimum hassle for a reconditioned engine, not only must all parts be assembled correctly, but they must be spotlessly clean....
To ensure maximum performance and minimum hassle for a reconditioned engine, not only must all parts be assembled correctly, but they must be spotlessly clean....
Engine — Assembly
1. Place the cylinder block on the bench, crankcase facing up. 2. Position the upper main bearing shells in the crankcase so that the tabs fit into the...
1. Place the cylinder block on the bench, crankcase facing up. 2. Position the upper main bearing shells in the crankcase so that the tabs fit into the...
Engine — preparation for start after repair
Note: Before starting the engine, see Chapter 25, paragraph 80 . 1. Check all connections to make sure there are no rags or tools left in the engine...
Note: Before starting the engine, see Chapter 25, paragraph 80 . 1. Check all connections to make sure there are no rags or tools left in the engine...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections of other Audi car models:
Power unit: Engines 4-cylinder Audi 100 C3 (1982-1990)
Diesel engines: 4 cylinder engines Audi A6 C4 (1994-1997)
Power unit: Engines 4-cylinder Audi 100 C3 (1982-1990)
Diesel engines: 4 cylinder engines Audi A6 C4 (1994-1997)
Share information:
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Power unit
- Engine
- Cooling system
- Heating and ventilation
- Petrol injection
- Diesel fuel system
- Fuel system
- Exhaust systems
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Suspension and steering wheel
- Body
- Body and trim
- Electrical equipment
- Electrical system
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Repair characteristics
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Gasoline engine
- Diesel engine
- Engine lubrication system
- Fuel system (gasoline)
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Ignition system
- Cooling system
- Heater
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch and gearbox
- Chassis
- Steering
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Body
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine 4-cylinder
- Engine 5-cylinder
- Cooling system
- Fuel and exhaust systems
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical transmission
- Automatic transmission
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
AudiManual.ru © 2017-2024 · Mobile version · Feedback · Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU · Site search · News and articles
80 B2 · 80 B3 petrol · 80 B3 · 80 B4 · 100 C3 diesel · 100 C3 petrol · 100 C3 · 100 C4 petrol · 100 C4 · A3 Type 8L · A4 B5 petrol · A4 B5 · A4 B6 petrol · A4 B6 · A6 C4 · A6 C5 · A6 C5 Allroad · A8 D2 · Q5 Type 8R · Audi A2 · 1.153
80 B2 · 80 B3 petrol · 80 B3 · 80 B4 · 100 C3 diesel · 100 C3 petrol · 100 C3 · 100 C4 petrol · 100 C4 · A3 Type 8L · A4 B5 petrol · A4 B5 · A4 B6 petrol · A4 B6 · A6 C4 · A6 C5 · A6 C5 Allroad · A8 D2 · Q5 Type 8R · Audi A2 · 1.153